The WORM Project has developed a plug and play framework designed to help humanitarian organisations manage medical waste more effectively during field hospital deployments. The framework connects operational needs with local waste management services, supporting both environmental sustainability and operational efficiency in complex humanitarian contexts.
A step-by-step decision support tool
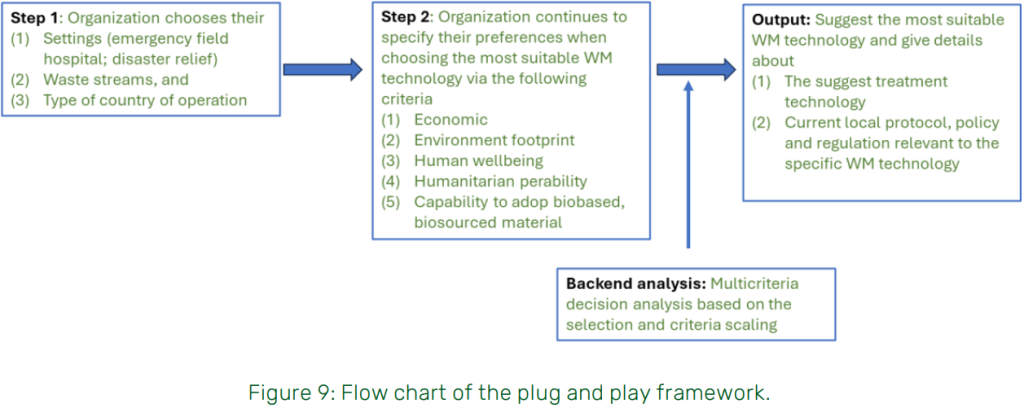
The framework is built on a multi-criteria decision analysis approach and a structured decision tree. It guides users in identifying the most appropriate waste treatment technologies and service providers through a three-step process:
- Set initial conditions: Define the operational context, including the type of waste stream, country of operation, and deployment model.
- Select and rate criteria: Stakeholders identify and weight decision factors such as economic efficiency, environmental footprint, regulatory alignment, and operability in humanitarian contexts.
- Generate recommendations: The system proposes suitable treatment technologies and lists available local waste management providers offering the recommended solutions, taking into account local policies and regulations.
Strengthening humanitarian–local partnerships
A key feature of the framework is its ability to bridge the gap between humanitarian actors and local waste management services, enabling faster and more informed decisions in the field. It provides structured guidance for choosing between on-site and off-site solutions and supports the integration of local infrastructure where available
Key recommendations
- Prioritise operability: The ability to maintain waste treatment operations under challenging field conditions is essential. Operability emerged as the most critical criterion for both humanitarian organisations and waste management companies.
- Use clear, shared criteria: Establishing transparent decision criteria can reduce misunderstandings and build trust between partners.
- Strengthen certification and guidance: A shared framework or certification process can help identify reliable local service providers and technologies.
- Deepen operability assessment: Future adoption can refine criteria to reflect more specific operational realities (e.g., combining autoclaving with landfill disposal), making the tool even more adaptive to different humanitarian settings.
By combining structured decision-making with local partnerships, the plug and play framework helps humanitarian organisations deploy more sustainable, context-appropriate, and resilient medical waste management strategies.